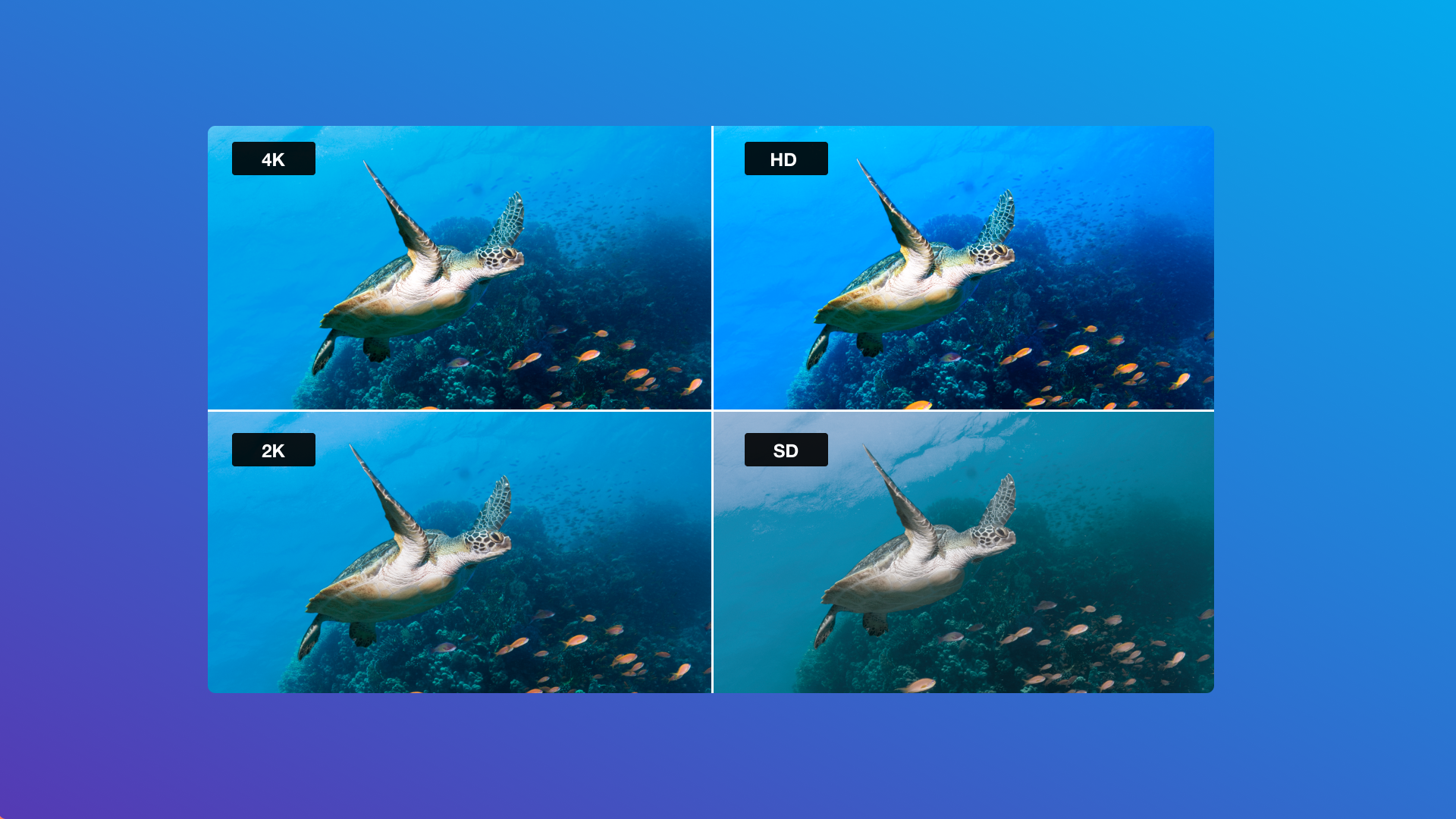
Video resolution and content quality go hand in hand—increasing the former also boosts the latter. Different resolutions suit different aspect ratios, making them more appropriate for some devices but not others.
Wading through all the specs for video sizes and formats can be daunting, so here’s a concise overview to simplify the learning process. Bookmark this article so you have a resource on hand when choosing a video’s resolution.
Upload a video to explore different resolutions →
What are pixels?
Pixels are tiny blocks that make up a screen. Each is composed of red, green, and blue lights that emit varying colors. For example, using a bit of red and a bit of blue, a pixel appears purple. This system enables each pixel to render over one billion colors on a 10-bit display.
Every device with a display has a certain number of pixels embedded into its screen. So a display with a resolution of 1920x1080 only has that many pixels—it’ll never display an image at 2560x1440, even if the image itself has those dimensions. Instead, it scales the image resolution down to the screen’s resolution, resulting in a loss of quality.
What’s video resolution?
Video resolution describes the number of pixels used to render each frame in a video. The more pixels a video uses, the sharper its details are because each pixel fills increasingly tiny portions to show even the finest details. This means 480p offers better picture quality than 360p which, in turn, offers better quality than 240p. These are all important factors when you're considering video compression.
For example, a 720p video is 1280x720 (1280 pixels horizontally x 720 vertically), so each frame has over 900,000 pixels. That same video captured at 1080p video resolution is 1,920x1080, resulting in frames with over two million pixels. That means every pixel will be smaller to fill in more information.
What’s the difference between ‘p’ and ‘i’ in resolutions?
The ‘p’ or ‘i’ in a resolution refers to the way a display screen renders an image. ‘p’ stands for “progressive,” which means the display renders the image from top to bottom. ‘i’ stands for “interlaced," meaning odd-numbered lines render first, followed by the even ones.
What’s aspect ratio?
Video aspect ratios describe the shape of an image based on the ratio between its width and height. A 1920x1080 image, for example, has a ratio of 16:9—there are 16 pixels along the width for every nine along the height.
The most common aspect ratios align with the screen sizes of popular devices so images can fill the screen. Here are the aspect ratios of standard devices:
- 4:3: Older television screens and computer displays.
- 16:9: Widescreen TVs and computer displays.
- 9:16: Smartphones.
- 21:9: Cinema screens and some high-end projectors.
Experiment with aspect ratios for free →
The most common video resolution sizes
Ideally, you’ll export your video in a format and resolution that suits your viewers’ devices. Nowadays, the following screen resolutions are most common among computer monitors, TVs, and smartphones.
Standard definition video resolution (SD)
Older displays use a 4:3 aspect ratio with the standard video resolution of 640x480 pixels, also known as 480i. As you may expect, that lower resolution doesn’t provide much clarity. Most SD screens today are no more than 20 inches diagonally, so every square inch of the screen consists of only about 120 pixels. Unless you're going for a retro look, it’s unlikely you’ll ever export a video in SD instead of HD.
High-definition video resolution (HD)
High-definition displays move into the 16:9 aspect ratio with a 1280x720 screen resolution, also known as 720p. HD displays come in several sizes, from handheld gaming devices like the Nintendo Switch to midsize TVs.
Speed is the main reason to export a project in 720p video resolution. The smaller file size will load faster on web pages, making it perfect for social media ads or live streaming. If your video is played on a small or medium-sized display and needs to load quickly, 720p is your best bet. That’s because on smaller screens, differences in resolution are near-imperceptible for humans, so it’s not necessary to use a higher resolution. For larger screens, you might want to use full high-definition.
High dynamic range (HDR) and standard dynamic range (SDR)
High dynamic range (HDR) imaging uses a set of techniques for shooting pictures and videos in a greater range of luminosity than SDR or standard dynamic range. Although SDR is the standard for displays, it provides only a fraction of the video and image dynamic range that HDR offers. This is why HDR is quickly replacing it.
In simple words: HDR quality content offers greater brightness and color range than SDR, making it more visually dope than SDR. Pictures and videos captured in HDR show a lot more details (even if it’s dark) than the standard dynamic range.
For creators, this means HDR videos bring more life to their story, capturing it in vibrant colors and maximum detail.
Full high-definition (FHD)
Full HD video resolution is the most common among today’s computer monitors and smartphones. It uses an aspect ratio of 16:9 with 1920x1080 resolution, also known as 1080p. Manufacturers use this resolution because it provides a fair balance of clarity and affordability, but it looks best on devices under 32 inches diagonally.
A 1080p video is excellent when you need detailed videos and are willing to potentially sacrifice load times to get them (most internet providers can support 1080p videos, but viewers in remote locations or with weak WiFi might struggle). This resolution is great for live streaming if your hardware can handle it or for video tutorials so viewers can clearly see what you’re demonstrating.
2K video resolution (QHD)
2K is another display resolution that uses the 16:9 aspect ratio. Its pixel dimensions are 2560x1440, so it’s also referred to as 1440p. This resolution typically appears on computer monitors intended for gaming, where the added resolution offers crisper graphics. The “Q” stands for “Quad” because QHD has four times the number of pixels as an HD screen.
If you’re a content creator making videos with in-game footage, you’ll probably want to export your videos in 1440p since your target audience will likely have a display that can take advantage of the higher resolution.
4K video resolution (Ultra HD)
At this level of resolution, we move into high-end displays, where affordability takes a back seat. 4K displays have an incredible 3840x2160 resolution, which is excellent for large TVs. You’ll only want to output videos in 4K if you intend for your viewers to watch them on a TV or very high-end computer monitor.
Editing a 4K video requires significant hardware capabilities, like a powerful CPU, ample RAM, and fast storage. A high-end graphics card can accelerate rendering and playback, especially in GPU-optimized editing software. A high-refresh-rate 4K monitor and a well-optimized workflow (proxy files, optimized media) can enhance the editing experience.
8K video resolution (Full Ultra HD)
You’ll be hard-pressed to find a device with genuine 8K, 7580x4320 resolution, much less content with native 8K adaptability. Even high-budget Hollywood cameras only shoot in 4K, meaning anything you watch on an 8K display must be upscaled to fit.
Diminishing returns kick in at this point in the resolution scale because only the largest screens will show a noticeable difference in clarity over 4K. Unless you’re making a tech demo for an 8K display, you’ll likely not need to export a video in 8K.
Upload your videos now →
FAQs
Is 1080p the same as 1280x720?
No. 1080p is full high-definition (FHD), with a display resolution of 1920x1080 pixels. 1280x720 are the dimensions for basic high-definition (HD), also known as 720p.
What are the resolutions, from lowest to highest?
Here are the most common resolutions, from lowest to highest:
- Standard definition (SD):
- Aspect ratio: 4:3
- Pixel dimensions: 640x480
- Resolution: 480p
- High-definition (HD):
- Aspect ratio: 16:9
- Pixel dimensions: 1280x720
- Resolution: 720p
- Full high-definition (FHD):
- Aspect ratio: 16:9
- Pixel dimensions: 1920x1080
- Resolution: 1080p
- 2K (QHD):
- Aspect ratio: 16:9
- Pixel dimensions: 2560x1440
- Resolution: 1440p
- 4K (UHD):
- Aspect ratio: 16:9
- Pixel dimensions: 3840x2160
- Resolution: 2160p
- 8K (UHD):
- Aspect ratio: 16:9
- Pixel dimensions: 7580x4320
- Resolution: 4320p
Is a higher resolution always best?
Not necessarily—the best resolution depends on where you intend to publish your content, as well as your audience’s internet speed and viewing device. A 720p HD resolution is ideal for web pages where fast loading times matter, especially for users with slower internet connections. For a feature film, 4K ensures every little detail is captured—which is perfect for large screens and high-speed connections. And 1080p is a great middle-ground, offering a balance of clarity and performance across most devices.
Is Youtube 16x9 or 4x3?
YouTube’s default aspect ratio is 16:9 to match the widescreen displays typical of modern monitors, and YouTube Shorts are in 9:16. The platform supports 4:3 videos but places black bars on either side of the image to fix the ratio.
Create stunning videos in seconds with Vimeo’s browser-based editor
Video resolution is one of several aspects unique to every video editing project you take on. Some, like brief social media ads, benefit from being a lightweight 720p, while editing a feature film will require the excellent quality afforded by 4K.
Vimeo’s free video editor gives you all the options you need to edit and export videos in a wide variety of resolutions. You can also use it to crop your content to fit different aspect ratios and fine-tune it for any platform.